S3
- What is Amazon S3?
- AWS SDK for Java 2.x
- AWS SDK for Java 2.x; Use asynchronous programming
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) provides object storage, which is built for storing and recovering any amount of information or data from anywhere over the internet. It provides this storage through a web services interface. While designed for developers for easier web-scale computing, it provides 99.999999999 percent durability and 99.99 percent availability of objects. It can also store computer files up to 5 terabytes in size.
Amazon S3 Concepts
- Buckets
- Objects
- Keys
- Regions
- Data Consistency Model
Buckets
- A bucket is a container used for storing the objects.
- Every object is incorporated in a bucket.
- For example, if the object named photos/tree.jpg is stored in the treeimage bucket, then it can be addressed by using the URL http://treeimage.s3.amazonaws.com/photos/tree.jpg.
- A bucket has no limit to the amount of objects that it can store. No bucket can exist inside of other buckets.
- S3 performance remains the same regardless of how many buckets have been created.
- The AWS user that creates a bucket owns it, and no other AWS user cannot own it. Therefore, we can say that the ownership of a bucket is not transferrable.
- The AWS account that creates a bucket can delete a bucket, but no other AWS user can delete the bucket.
Objects
- Objects are the entities which are stored in an S3 bucket.
- An object consists of object data and metadata where metadata is a set of name-value pair that describes the data.
- An object consists of some default metadata such as date last modified, and standard HTTP metadata, such as Content type. Custom metadata can also be specified at the time of storing an object.
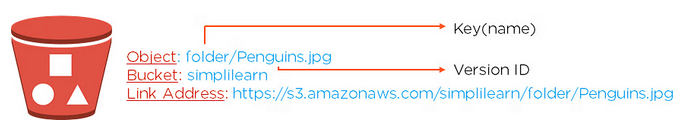
- It is uniquely identified within a bucket by key and version ID.
Key
- A key is a unique identifier for an object.
- Every object in a bucket is associated with one key.
- An object can be uniquely identified by using a combination of bucket name, the key, and optionally version ID.
- For example, in the URL http://jtp.s3.amazonaws.com/2019-01-31/Amazons3.wsdl where "jtp" is the bucket name, and key is "2019-01-31/Amazons3.wsdl"
Regions
- You can choose a geographical region in which you want to store the buckets that you have created.
- A region is chosen in such a way that it optimizes the latency, minimize costs or address regulatory requirements.
- Objects will not leave the region unless you explicitly transfer the objects to another region.
🗃️ Examples
2 items
📄️ References
https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/aws-tutorial/aws-s3