Terminate Operations
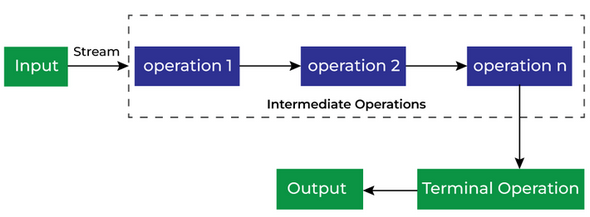
The terminal operations of the Java Stream interface typically return a single value.
List of stream Terminate operations:
-
anyMatch()
Syntax:
boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
Stream anyMatch(Predicate predicate) returns whether any elements of this stream match the provided predicate.
public void streamAnyMatch() {
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>();
stringList.add("Java Guides");
stringList.add("Python Guides");
stringList.add("C Guides");
Stream<String> stream = stringList.stream();
boolean anyMatch = stream.anyMatch((value) -> { return value.startsWith("Java"); });
System.out.println(anyMatch);
}
-
allMatch()
Syntax:
boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
The allMatch() method returns always a true or false, based on the result of the evaluation.
public void streamAllMatch() {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("one", "two", "three", "four");
Predicate<String> containsDigit = s -> s.contains("\\d+") == false;
boolean match = stream.allMatch(containsDigit);
System.out.println(match);
}
-
allMatch()
Syntax:
boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
The allMatch() method returns always a true or false, based on the result of the evaluation.
public void collectToMap01() {
Stream<String> s = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "orange");
Map<Character, String> m = s.collect(Collectors.toMap(s1 -> s1.charAt(0), s1 -> s1));
System.out.println(m);
}
// IllegalStateException - duplicate keys
public void collectToMap02() {
Stream<String> s = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "apricot", "orange");
Map<Character, String> m = s.collect(Collectors.toMap(s1 -> s1.charAt(0), s1 -> s1));
System.out.println(m);
}
public void collectToMap03() {
Stream<String> s = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "apricot", "orange", "apple");
Map<Character, String> m = s.collect(Collectors.toMap(s1 -> s1.charAt(0),
s1 -> s1,
(s1, s2) -> s1 + "|" + s2));
System.out.println(m);
}
public void collectToMap04() {
Stream<String> s = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "apricot", "orange", "apple");
LinkedHashMap<Character, String> m = s.collect(
Collectors.toMap(s1 -> s1.charAt(0),
s1 -> s1,
(s1, s2) -> s1 + "|" + s2,
LinkedHashMap::new));
System.out.println(m);
}
-
noneMatch()
Syntax:
boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
public void streamNoneMatch() {
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("one", "two", "three", "four");
boolean answer = stream.noneMatch(str -> (str.length() == 10));
System.out.println(answer);
}
-
collect()
Syntax:
<T,K,U> Collector<T,?,Map<K,U>> toMap(Function<? super T,? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T,? extends U> valueMapper)
<T,K,U> Collector<T,?,Map<K,U>> toMap(Function<? super T,? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T,? extends U> valueMapper,
BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction)
<T,K,U,M extends Map<K,U>> Collector<T,?,M> toMap(Function<? super T,? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T,? extends U> valueMapper,
BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction,
Supplier<M> mapSupplier)
Parameters:
keyMapper: A mapping function to produce the map keys for each input stream element.
valueMapper: A mapping function to produce the map values for each input stream element.
mergeFunction: A binary operator which is to resolve collisions between values associated with the same key. The inputs to this function are the values which belong to the same key.
mapSupplier: A function which provides a new instance of the desired implementation of the Map.
The method:
// if there are duplicate keys as provided by keyMapper function.
Collectors.toMap(keyMapper, valueMapper) throw IllegalStateException
public void collectToMap01() {
Stream<String> s = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "orange");
Map<Character, String> m = s.collect(Collectors.toMap(s1 -> s1.charAt(0), s1 -> s1));
System.out.println(m);
}
// IllegalStateException - duplicate keys
public void collectToMap02() {
Stream<String> s = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "apricot", "orange");
Map<Character, String> m = s.collect(Collectors.toMap(s1 -> s1.charAt(0), s1 -> s1));
System.out.println(m);
}
public void collectToMap03() {
Stream<String> s = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "apricot", "orange", "apple");
Map<Character, String> m = s.collect(Collectors.toMap(s1 -> s1.charAt(0),
s1 -> s1,
(s1, s2) -> s1 + "|" + s2));
System.out.println(m);
}
public void collectToMap04() {
Stream<String> s = Stream.of("apple", "banana", "apricot", "orange", "apple");
LinkedHashMap<Character, String> m = s.collect(
Collectors.toMap(s1 -> s1.charAt(0),
s1 -> s1,
(s1, s2) -> s1 + "|" + s2,
LinkedHashMap::new));
System.out.println(m);
}
-
count()
public void streamCount() {
List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 7, 9, 22, 19, 18, 47, 3, 12, 29, 17, 44, 78, 99));
long count = numbers.stream().count();
System.out.println(count);
}
-
distinct
Method to find all instances of a class with unique id.
// Get distinct people by id
public void streamDistinct() {
Person doeOne = new Person(1, "John", "Doe");
Person doeTwo = new Person(1, "John", "Doe");
Person doeThree = new Person(1, "John", "Doe");
Person brianOne = new Person(2, "Brian", "Clooney");
Person brianTwo = new Person(2, "Brian", "Clooney");
Person alex = new Person(3, "Alex", "Kolen");
Collection<Person> list = Arrays.asList(
alex,
brianOne,
brianTwo,
doeOne,
doeTwo,
doeThree);
List<Person> distinctElements = list.stream()
.distinct()
.collect( Collectors.toList() );
System.out.println( distinctElements );
}
-
groupingFindDuplicatesS(stream)
public void streamDuplicates() {
// Initial stream
Stream<Integer> stream = Stream.of(5, 13, 4, 21, 13, 27, 2, 59, 59, 34);
// Print the found duplicate elements
System.out.println(groupingFindDuplicatesS(stream));
}
-
findFirst()
public void streamFindFirst() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 2, 1);
Optional<Integer> first = list
.stream()
.filter(x -> x > 1).findFirst();
if (first.isPresent()) {
System.out.println(first.get()); // 2
} else {
System.out.println("no value?");
}
}
-
findAny()
public void streamFindAny() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 2, 1);
Optional<Integer> any = list.stream().filter(x -> x > 1).findAny();
if (any.isPresent()) {
Integer result = any.get();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
-
forEach()
forEach() method is used to iterate or loop each element of Collection or Map or Stream.
public void streamForEach() {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("John");
list.add("Oliver");
list.add("Jack");
list.add("Henry");
list.stream().forEach(value -> System.out.println(value));
}
-
min()
Syntax:
Optional<T> min(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
public void streamMax() {
List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(14, 98, 72, 8, 3, 1, 10, 14, 42, 97, 24));
int maxNumber = numbers.stream()
.max(Comparator.comparing(Integer::valueOf))
.get();
System.out.println(maxNumber);
}
-
max()
Syntax
Optional<T> max(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
public void streamMax() {
List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(14, 98, 72, 8, 3, 1, 10, 14, 42, 97, 24));
int maxNumber = numbers.stream()
.max(Comparator.comparing(Integer::valueOf))
.get();
System.out.println(maxNumber);
}
-
reduce()
Syntax:
reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
// identity – an element that is the initial value of the reduction operation and the default result if the stream is empty
// accumulator – It’s a BinaryOperator. It represents a function that takes two parameters, the first is the result of a previous reduction operation, and the second is the next element in the stream.
public void streamReduce() {
List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(3, 5, 7, 9));
int result = numbers.stream().reduce(1, (num1, num2) -> num1 * num2);
System.out.println(result);
}
-
sum()
public void streamSum() {
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Integer sum = integers.stream()
.mapToInt(Integer::intValue)
.sum();
System.out.println(sum);
}
-
average(
public void streamAverage() {
IntStream stream = IntStream.of(1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8);
OptionalDouble obj = stream.average();
if (obj.isPresent()) {
System.out.println(obj.getAsDouble());
} else {
System.out.println("-1");
}
}